I’ve installed a OpenShift 4.16.46 cluster this round to support a customer in their OSD removal issue. The rook-ceph toolbox is a pod with common tools used for debugging, testing, and troubleshooting a Ceph cluster.
Official Reference: https://access.redhat.com/articles/4628891
Red Hat does not support running Ceph commands in OpenShift Data Foundation clusters (unless indicated by Red Hat support or Red Hat documentation) as it can cause data loss if you run the wrong commands. In that case, the Red Hat support team is only able to provide commercially reasonable effort and may not be able to restore all the data in case of any data loss.
ODF v4.15 and above, to enable the toolbox pod, patch/edit the StorageCluster CR like below:
oc patch storagecluster ocs-storagecluster -n openshift-storage --type json --patch '[{ "op": "replace", "path": "/spec/enableCephTools", "value": true }]'
ODF with Portworx
oc patch storageclusters.ocs.openshift.io ocs-storagecluster -n openshift-storage --type json --patch '[{ "op": "replace", "path": "/spec/enableCephTools", "value": true }]'Confirm healthy & headroom
kubens openshift-storage
oc rsh deploy/rook-ceph-tools ceph -s
oc deploy/rook-ceph-tools ceph osd tree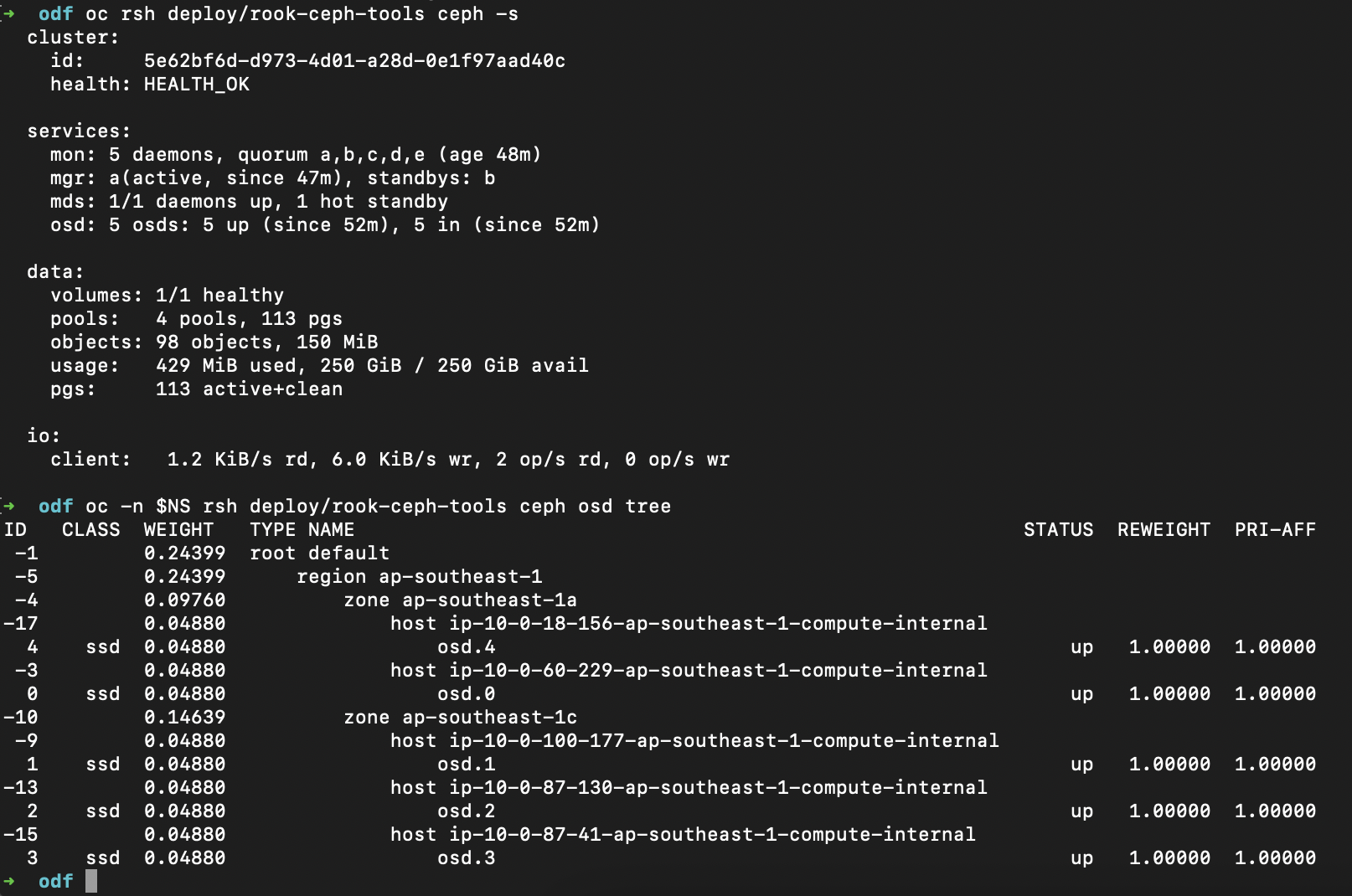
- Aim for
HEALTH_OK(orWARNat most), and enough free space.
Note: with exactly 3 OSDs and poolsize=3(default), losing 1 OSD leaves you degraded (min_size=2) and Ceph cannot restore full 3x replication until you replace/add an OSD.
List OSD pods & where they run
oc get pods -l app=rook-ceph-osd -o wide
Map OSD → PVC → PV → node

Refer to the other blog post for this script (stitch.sh)
ODF on AWS EBS or RAW EBS volume (Bare Disk)
You might have noticed that my ODF is installed on AWS where it is using raw EBS volumes to the worker nodes. This is using LSO with storageclass to expose them. ODF consumes those PVs and treats them as if they were bare disks.
I could have directly provision EBS gp3 volumes for OSDs without the need for LSO and it’s LocalVolumeSets.
Both works, but they’re different operating modes:
- If your cluster is IPI on AWS and you want managed, elastic scaling, do it with cloud-native AWS EBS. Just make sure you have 3 worker nodes installed across 3 different AZs for better resilience. ODF on AWS uses the “AWS StorageCluster” mode that provisions gp3 volumes for OSDs.
- If you already pre-attached volumes and want to treat them like bare metal (maybe to control disk size/placement yourself), you can keep to self-attached EBS volumes to your EC2 instances.
Okay… I did not provision NFS.